2022年01月24日 力扣每日一题
题目
城市用一个 双向连通 图表示,图中有 n 个节点,从 1 到 n 编号(包含 1 和 n)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中每个 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示一条节点 ui 和节点 vi 之间的双向连通边。每组节点对由 最多一条 边连通,顶点不存在连接到自身的边。穿过任意一条边的时间是 time 分钟。
每个节点都有一个交通信号灯,每 change 分钟改变一次,从绿色变成红色,再由红色变成绿色,循环往复。所有信号灯都 同时 改变。你可以在 任何时候 进入某个节点,但是 只能 在节点 信号灯是绿色时 才能离开。如果信号灯是 绿色 ,你 不能 在节点等待,必须离开。
第二小的值 是 严格大于 最小值的所有值中最小的值。
- 例如,
[2, 3, 4]中第二小的值是3,而[2, 2, 4]中第二小的值是4。
给你 n、edges、time 和 change ,返回从节点 1 到节点 n 需要的 第二短时间 。
注意:
- 你可以 任意次 穿过任意顶点,包括
1和n。 - 你可以假设在 启程时 ,所有信号灯刚刚变成 绿色 。
示例 1:
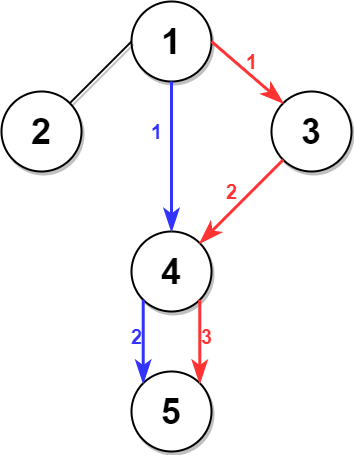
输入:n = 5, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[3,4],[4,5]], time = 3, change = 5 输出:13 解释: 上面的左图展现了给出的城市交通图。 右图中的蓝色路径是最短时间路径。 花费的时间是: - 从节点 1 开始,总花费时间=0 - 1 -> 4:3 分钟,总花费时间=3 - 4 -> 5:3 分钟,总花费时间=6 因此需要的最小时间是 6 分钟。 右图中的红色路径是第二短时间路径。 - 从节点 1 开始,总花费时间=0 - 1 -> 3:3 分钟,总花费时间=3 - 3 -> 4:3 分钟,总花费时间=6 - 在节点 4 等待 4 分钟,总花费时间=10 - 4 -> 5:3 分钟,总花费时间=13 因此第二短时间是 13 分钟。
示例 2:

输入:n = 2, edges = [[1,2]], time = 3, change = 2 输出:11 解释: 最短时间路径是 1 -> 2 ,总花费时间 = 3 分钟 最短时间路径是 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 2 ,总花费时间 = 11 分钟
提示:
2 <= n <= 104n - 1 <= edges.length <= min(2 * 104, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi- 不含重复边
- 每个节点都可以从其他节点直接或者间接到达
1 <= time, change <= 103
Related Topics
个人解法
{% tabs categories%}
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int secondMinimum(int n, int[][] edges, int time, int change) {
// 统计所有节点的联通节点,并将其存入map中留着后面使用
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
map.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
map.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
map.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(1);
// 记录节点到达的次数
int[] counts = new int[n + 1];
// 记录到达节点的时间
int free = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 红灯情况下加上需要等待的时间
if (free % (2 * change) >= change) {
free += change - free % change;
}
free += time;
// 同一时间可以到达的节点数量
int size = queue.size();
// 同一时间节点是否已经到达
boolean[] use = new boolean[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 获取该节点接下来可以到达的节点
List<Integer> list = map.get(queue.poll());
for (int num : list) {
// 同一时间未到达,并且到达该节点的总次数小于2
if (!use[num] && counts[num] < 2) {
queue.add(num);
use[num] = true;
counts[num]++;
}
// 如果是第二次到达最后一个节点,直接返回需要到达的诗句
if (num == n && counts[num] == 2) {
return free;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
from collections import deque
from typing import List
class Solution:
def secondMinimum(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], time: int, change: int) -> int:
# 统计所有节点的联通节点,并将其存入map中留着后面使用
maps = [[0] for _ in range(n + 1)]
for edge in edges:
maps[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
maps[edge[1]].append(edge[0])
queue = deque()
queue.append(1)
# 记录节点到达的次数
counts = [0] * (n + 1)
# 记录到达节点的时间
free = 0
while len(queue):
# 红灯情况下加上需要等待的时间
if free % (2 * change) >= change:
free += change - free % change
free += time
# 同一时间可以到达的节点数量
size = len(queue)
# 同一时间节点是否已经到达
use = [False] * (n + 1)
for i in range(size):
for num in maps[queue.popleft()]:
# 同一时间未到达,并且到达该节点的总次数小于2
if use[num] is False and counts[num] < 2:
queue.append(num)
use[num] = True
counts[num] += 1
# 如果是第二次到达最后一个节点,直接返回需要到达的诗句
if num == n and counts[num] == 2:
return free
return 0
{% endtabs %}
